

Stone Surgery
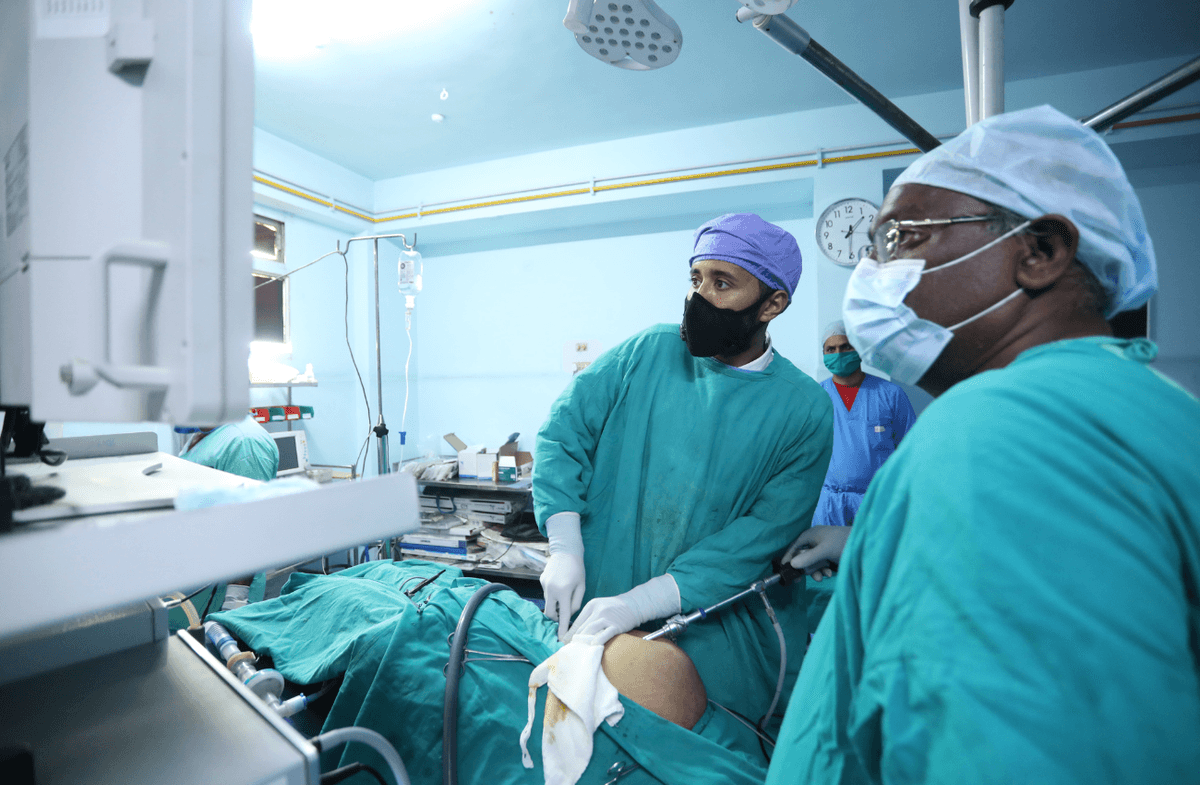
Stone surgery, also known as kidney stone removal, is performed to remove kidney stones that are too large to pass naturally or cause significant pain or complications. There are several surgical methods, including extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), which uses sound waves to break the stones into smaller pieces, ureteroscopy, where a thin scope is inserted to remove or break up the stone, and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), which involves a small incision to remove larger stones directly from the kidney. Recovery depends on the procedure used, but patients typically resume normal activities within a few days to weeks.
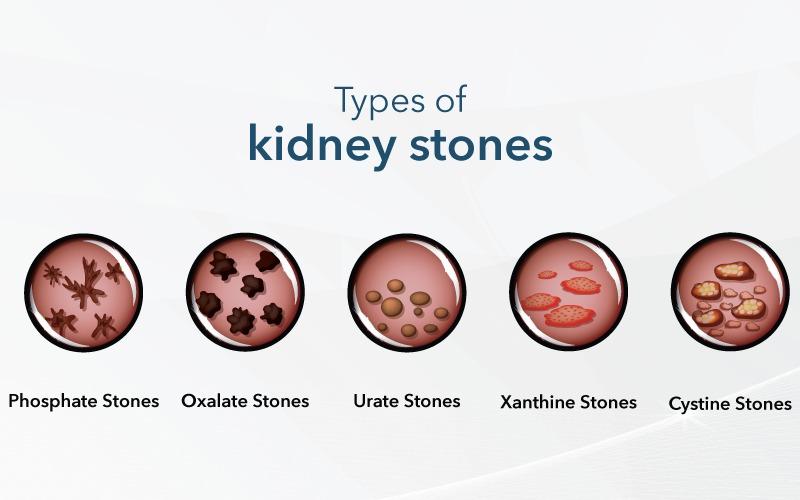
There are several types of kidney stones, including:
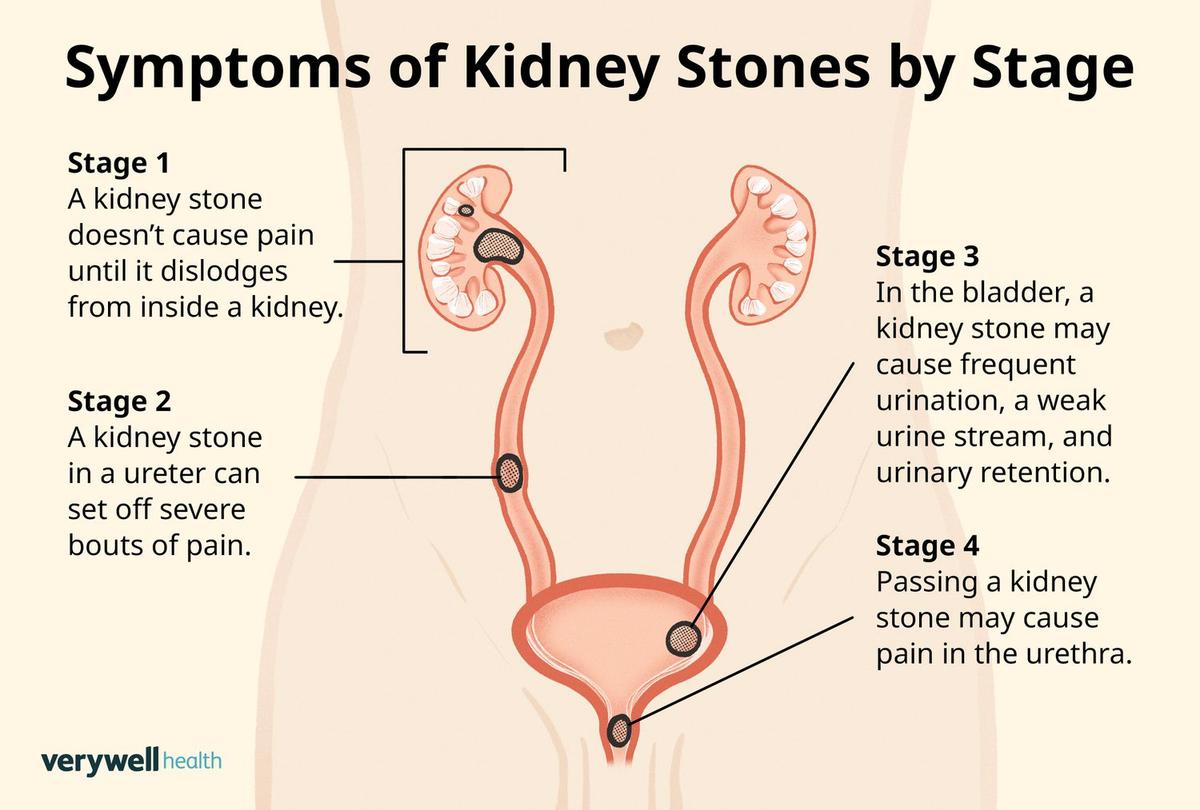
Kidney: The most common symptom of kidney stones is severe pain in the back and side, often radiating to the lower abdomen and groin. This pain can come in waves and may be accompanied by:
Gall Bladder:

Kidney: Several factors can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, including:
Gall Bladder Stone:
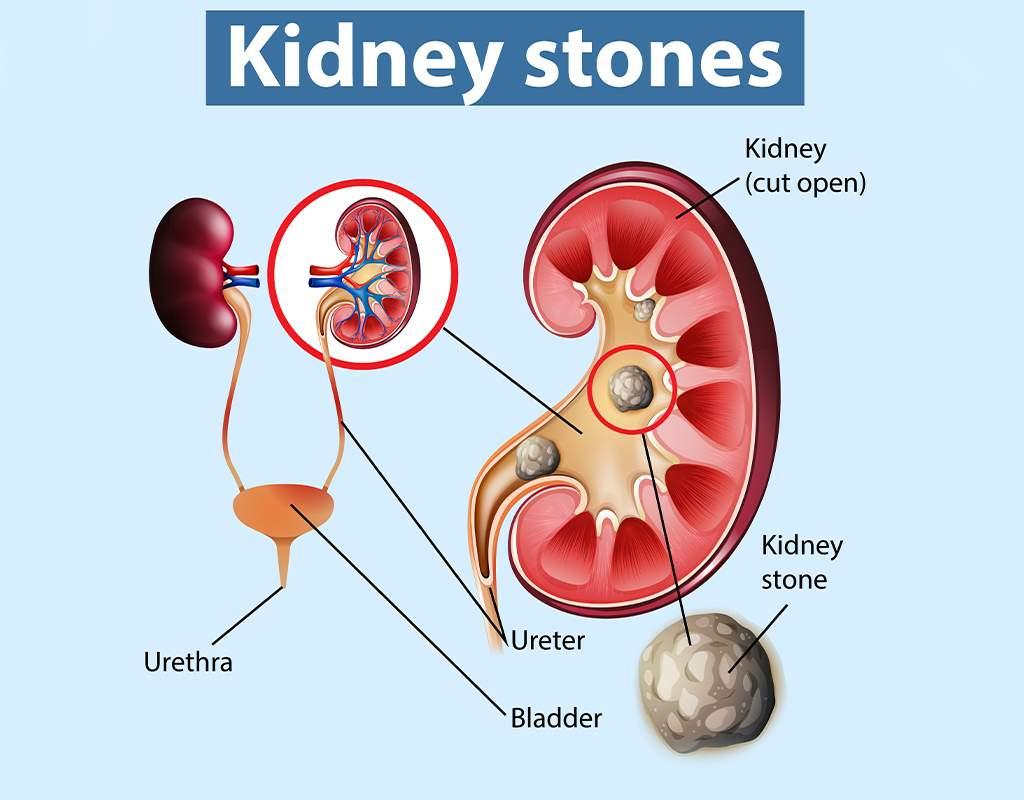
The treatment approach for kidney stones depends on factors such as the size, type, and location of the stone, as well as the severity of symptoms.

I am Arpit Bansal, a doctor, specialized in advanced laparoscopic, cancer, and laser surgery. With a Fellowship from the UK, i am future-ready for robotic surgeries. I have trained under some of the finest surgeons in India.
Kidney stones can cause severe pain, often described as sharp and intense, usually in the back or side. Other common symptoms include frequent urination, painful urination, blood in the urine, nausea, and vomiting.
Kidney stones form when substances in urine, like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, crystallize and stick together. This can be caused by factors such as dehydration, diet, certain medical conditions, and family history.
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL) is a non-invasive procedure used to break kidney stones into smaller pieces. These smaller pieces can then pass through the urinary tract more easily.
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water daily. However, your specific water needs may vary based on factors like activity level, climate, and overall health.
To prevent kidney stones, drink plenty of water, reduce sodium intake, limit animal protein, and consume a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.