Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside an ovary. While many ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can cause symptoms, complications, or even interfere with fertility. This article will help you understand the types of ovarian cysts, their symptoms, causes, and the best treatment options in India, especially under expert care such as that provided by Dr. Arpit Bansal.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
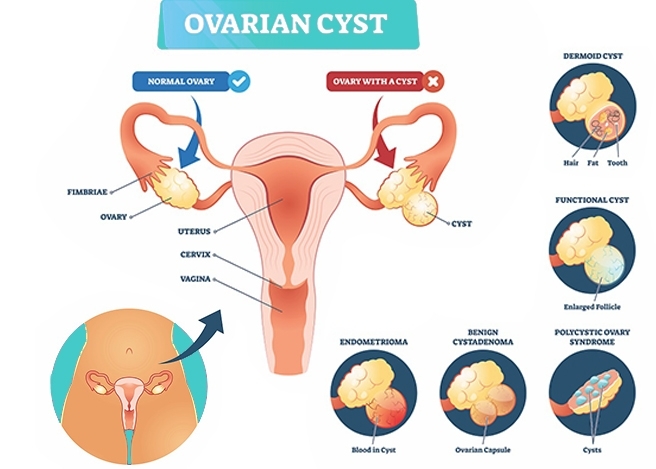
An ovarian cyst is a sac or pocket within or on the surface of an ovary that contains fluid or semisolid material. Most women will have one or more ovarian cysts in their lifetime. Many cysts are functional (related to the menstrual cycle) and not danger signals. However, some may require evaluation and treatment depending on size, type, symptoms, and potential risks of complications such as rupture or ovarian torsion.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Here are the main types of ovarian cysts you should know about:
Functional Cysts
These are the most common and usually benign. They include:
Follicular Cysts: Form when a follicle fails to release an egg and instead continues to grow.
Corpus Luteum Cysts: After ovulation, the follicle transforms into the corpus luteum; sometimes fluid accumulates and the “corpus luteum” becomes cystic.
Endometriomas
These develop in women with endometriosis. Uterine lining tissue grows outside the uterus (for example, on the ovaries), leading to cyst formation usually filled with dark, chocolate-colored fluid. They can cause pain, menstrual irregularities, and fertility issues.
Dermoid Cysts (Mature Cystic Teratomas)
These contain various tissues like hair, teeth, sebaceous materials or fat, since they are formed from embryonic cells. They are usually benign but as they grow they may cause pain or complications.
Cystadenomas
These develop from the surface epithelial tissue of the ovary. They can be filled with watery or mucous-like fluid. Though often benign, some cystadenomas can grow large and cause discomfort.
Polycystic Ovaries (in PCOS)
In Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), the ovaries have many small cysts due to hormonal imbalances. These are typically multiple small follicles rather than a single large cyst. PCOS often has other accompanying symptoms like irregular periods, acne, and fertility challenges.
Pathologic or Neoplastic Cysts
Less common, sometimes ovarian cysts can become pathological or even cancerous. Features such as solid components, irregular walls, rapid growth, or occurrence after menopause raise suspicion.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic. But when symptoms appear, they can vary depending on the type, size, and position of the cyst. Here are typical symptoms:
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain; may be dull, aching, or sharp on one side.
Bloating, swelling or feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
Irregular menstrual cycle, heavy or light periods, spotting between periods.
Pain during sexual intercourse.
Painful bowel movements, constipation or pressure on the bowel.
Frequent or urgent urination if the cyst presses on the bladder.
Nausea or vomiting in cases of torsion or rupture.
Causes & Risk Factors
What contributes to the formation of ovarian cysts?
Hormonal imbalances
Fluctuating levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone are implicated, especially in functional cysts or PCOS.
Endometriosis
Tissue similar to uterine lining growing outside the uterus can attach to ovaries and cause endometriomas.
Pregnancy
Some cysts, especially corpus luteum cysts, form during early pregnancy.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
A common hormonal disorder that results in multiple small cysts on ovaries.
Pelvic infections
Severe infections spreading to ovaries can trigger cyst formation.
Age and Medical History
Cysts are more common during reproductive age. Previous cysts increase risk. Some cysts may become more risky after menopause.
When to See a Doctor
While many cysts resolve naturally, certain symptoms or situations call for immediate medical attention:
Sudden severe abdominal or pelvic pain (might indicate rupture or torsion)
Fever, vomiting, dizziness alongside pain (could suggest infection or serious complication)
Rapid increase in abdominal swelling or size
Symptoms persisting across several menstrual cycles without improvement
Suspicion of pathology or cancer (especially in older women)
Treatment Options in India (Including at Dr. Arpit Bansal’s Clinic)
Treatment depends on the type of cyst, its size, symptoms, risk factors (including age, fertility desires), and findings on diagnostic imaging.
Watchful Waiting / Observation
For small, functional cysts that are asymptomatic, doctors may recommend regular ultrasounds (e.g., after 1-3 menstrual cycles) to monitor changes.
Most functional cysts shrink naturally.
Medication
Hormonal contraceptives or birth control pills: regulate cycle, prevent formation of new cysts.
Pain relievers (NSAIDs) to manage discomfort.
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Laparoscopy: small incisions (“key-hole surgery”) to remove cysts while preserving ovary. Faster recovery.
Laparotomy: open surgery, used when cysts are large, complex, or suspected cancerous.
Special Procedures
Cyst drainage or aspiration in select cases.
Removal of entire ovary (oophorectomy), in rare cases where cyst is malignant or damaging.
Fertility Preservation
For women who want children, preserving ovarian tissue when possible is important.
Choosing laparoscopic over open surgeries, and timely diagnosis are critical.
Lifestyle & Follow-Up
Regular gynecological checkups, ultrasound imaging.
Managing hormonal disorders, weight control, balanced diet.
Prompt medical consultation if symptoms worsen.
How Dr. Arpit Bansal Can Help
At Dr. Arpit Bansal’s clinic, you’ll find comprehensive care for ovarian cysts treatment in India. The approach includes accurate diagnosis via pelvic ultrasound (TVS/abdominal), hormonal assessments, minimally invasive surgical techniques where needed, and an emphasis on preserving fertility. Personalized treatment plans take into account patient’s age, cyst type & size, symptoms, and reproductive goals.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of ovarian cysts — from functional and dermoid to endometriomas and cystadenomas — helps in detecting risk early. By being aware of the symptoms and causes, women can seek timely medical care. Treatment options vary widely: many cysts resolve naturally, others may need medication or surgery. For those in India seeking ovarian cyst treatment, consulting experienced gynecologists like Dr. Arpit Bansal ensures evidence-based care with modern techniques.